Materials, environments, and textures add images, colors, lighting, and textures to parts of your model. Applying these effects to your models adds an extra level of detail and realism.
SketchUp’s default materials support Physically Based Rendering (PBR) texture maps. These materials can simulate the physical properties of surfaces like roughness or metalness. That means materials can be basic, like a color with some transparency, or as specific as you want them to be, like a Mediterranean flooring tile with deep grout lines. You can keep it simple and choose to paint a basic color to represent a surface (white for kitchen counters, gray for sinks). Or you can choose richer materials that simulate design elements like textured paint on an interior wall or the finish of wood paneling on the floor.
Adding an environment enhances SketchUp’s photoreal materials. The textures in materials react dynamically using an environment’s direction and quality of light and its virtual surroundings for reflections. Now, you have the ingredients to convey the feel of that siding texture and the finish of that wood paneling.
To get started with materials, textures, and environments, take a look at the following articles:
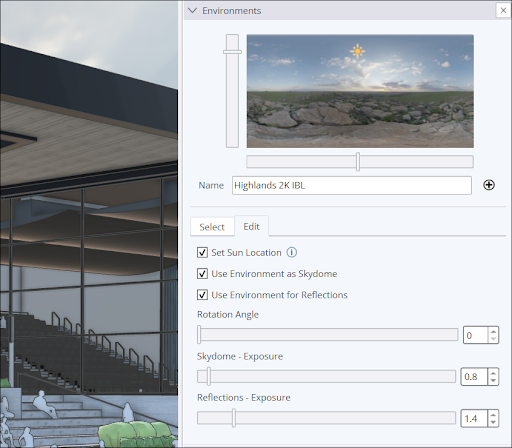
- Adding an Environment to a Model – SketchUp’s Environments panel contains a default collection of configurable environments and options to import environments your own.
- Navigating the Materials Panel – The Materials panel helps you find, manage, and even create materials for use in your SketchUp models.
- Applying Materials – Learn how to apply a material using the Paint Bucket tool and the Materials panel.
- Replacing a Material – A guide to replacing a material in your model with another material using the Materials panel.
- Create Your Own Materials – Learn how to create a material using your own images.
- Editing Materials – Each material is fully customizable. Learn about the options available in the Edit tab of the Materials panel and how to use them.
- Generate Textures – An AI service that helps transform a basic material into a photoreal material by creating and adding more textures.
- Positioning Textures – Learn how to wrap or project an image texture around an entity like a box or cylinder, or project a texture onto a curved surface.
- Managing and Organizing Materials – The Materials panel provides all you need to track the materials used in your model, clear out unwanted materials, and manage or create collections.
- Calculating Material Area – The Materials panel can help you calculate the surface area painted with each material you use.
- Importing and Using 2D Images – How to import and use a 2D image in your model.